Over a century ago, scientists and manufacturers were keen on discovering effective solvents for paints, coatings, and more. Butyl acetate stepped onto the scene as early industrialists searched for alternatives to older, harsher chemicals. As paint technology started to modernize, the need for something with better performance and less odor pushed butyl acetate up the ranks. Personal experience working with painters through the years showed how these choices make a difference. Older folks in the field still talk about how switching solvents in the mid-20th century wasn’t just about chemistry. It shaped job safety and product reliability across industries large and small.
Even those outside the chemical sector have run into butyl acetate, maybe without knowing it. This colorless liquid with a sweet, fruity smell pops up everywhere from nail polish remover to inks and adhesives. Its main allure for manufacturers rests on being a versatile solvent that evaporates at a manageable rate. Compared to similar products, I’ve noticed companies choose butyl acetate for balances between effectiveness and ease of use. It turns a tricky formulation into one that feels smooth in application and refinement.
Butyl acetate carries a straightforward structure. With four carbons on one end and an ester group on the other, it boils at about 126°C, offers moderate solubility in water, and burns with a faint blue flame. At room temperature, it’s a liquid that flows easily but doesn’t evaporate instantly, granting developers a bit of breathing room in large-scale operations. Its density stands close to 0.88 g/cm³, which allows it to stay put in most formulations without separating. Chemical stability keeps storage headaches low, and from my time in labs, I’ve seen how much easier inventory management is when products aren’t ticking time bombs.
On every drum or container, you’ll see butyl acetate’s CAS number—123-86-4—posted loud and clear, showing how invested the industry is in proper tracking. Manufacturers lean into batch-specific details, including purity percentages (usually topping 99%). Knowing how sensitive regulatory bodies can be, companies include hazard warnings and safety icons, with flammability getting special mention. I spent time helping a factory update its Safety Data Sheets, and the amount of scrutiny over labeling taught me not to cut corners. Even for something as widely used as butyl acetate, a missing label can hold up an entire shipment.
Most modern butyl acetate gets made by combining acetic acid with n-butanol, using a bit of acid catalyst to get the two to form the desired ester. Process engineers pour over their distillation columns and reactors, always adjusting pressures and temperatures to squeeze out the purest product. Watching production runs, I saw firsthand how a slight nudge in temperature changed yields noticeably. After finishing the reaction, distillation pulls off the water and unreacted material, leaving the main product. This straightforward process survives because it keeps production lines running smoothly rather than chasing marginal gains with complicated tweaks.
Chemists find butyl acetate resilient, but it’s not immune to strong acids or bases. Hydrolysis can break it down, giving back the original n-butanol and acetic acid. In everyday storage, this doesn’t cause much trouble, but product designers account for it when mixing butyl acetate with water-based paints. People with experience formulating products respect the line between stable uses and environments where unwanted breakdown could ruin a batch. On the modification side, chemists can tweak it to form related esters with different chain lengths, opening new possibilities in product development.
If you work with chemicals, you know how many names a single compound can pick up. Butyl acetate goes by butyl ethanoate, n-butyl acetate, and BA. Some product lines refer to it under brand-specific codes, further muddying the waters. I recall a case where a customer nearly bought the wrong solvent because they didn’t recognize one of the synonyms. Clarity in naming helps prevent expensive mistakes, whether it’s a small lab or a sprawling manufacturing plant.
Handling butyl acetate means paying attention to basics: proper ventilation, fire prevention, and skin protection. With a low flash point, it doesn’t take much for vapors to ignite, so storage rules and local fire codes aren’t just paperwork—they’re essential. I’ve seen what a container leak into a poorly ventilated shop does to both productivity and worker health. Safety glasses, gloves, and good airflow aren’t just recommendations—they’re real-world necessities, especially during transfer and cleanup. Regulations focus on permissible exposure limits, reflecting long conversations between industry, scientists, and regulators all aiming to keep people safe without overcomplicating standard practice.
Walk through any paint or coatings facility, and you’ll smell butyl acetate before you see the signage. Paints, varnishes, and coatings industries depend on its ability to dissolve resins and enable smooth application. Personal projects, including painting furniture or restoring surfaces, brought butyl acetate into play for its reliable solvency and manageable evaporation rate. Printing operations, adhesives, even flavors and fragrances use it for similar reasons. Its sweet scent finds a surprising home in artificial flavors and perfumes, making it one of those chemicals that crosses from factory floors to everyday consumer life. Having applied both professional paints and hobby glues, the ease of application owed to this component can’t be overstated.
Labs and innovation teams continue to push butyl acetate’s boundaries, experimenting with blends for low-VOC emissions or higher performance under harsh conditions. Technology upgrades in process equipment have improved recovery and recycling rates, cutting both costs and environmental impact. I’ve worked near research teams tasked with finding less hazardous alternatives, and their results often loop right back to butyl acetate’s balance of safety and performance. Development isn’t just about greener chemistry, though—it’s also about making formulations friendlier to the end user, with slower drying times or reduced odor for specific applications.
How safe is butyl acetate long-term? Toxicity research points towards low acute toxicity but recognizes that chronic exposure to high vapor concentrations can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, with headaches sometimes following long sessions in poorly ventilated rooms. Case studies from occupational settings highlight the need to maintain proper industrial hygiene. Over the years, updated reports have guided changes in workplace exposure limits, usually moving towards more protective standards. Even with years of relatively safe use, regulations adapt, and researchers won’t stop examining subtle health markers in both workers and communities living near production sites. Precise, long-term studies matter since trends in health complaints sometimes appear slowly.
Looking ahead, butyl acetate won’t disappear from paints, coatings, and adhesives any time soon, though the push for better environmental outcomes gains momentum. Blends with bio-derived n-butanol or acetic acid already turn up in specialized markets. Regulatory pressures and sustainability trends encourage researchers to develop biodegradation pathways and minimize emissions. Real change, though, might stem from advances in process efficiency—energy use, waste reduction, and safer containment can give the sector a cleaner footprint. Experience shows that most actors in the field listen to market signals, balancing responsibility with the practical demands of production. As research pours in and as buyers value safety more, butyl acetate’s story isn’t over—the next chapters will blend old strengths with newly minted green chemistry.
Walk into a hardware store, and you’ll probably catch a whiff of butyl acetate. It’s the sweet, fruity smell in many paints and nail polishes. People know butyl acetate mainly as a solvent that helps things dry quickly and spread evenly. It helps paint glide onto walls, wood, and metal. Once, I painted my kitchen cabinets, and the quick-dry finish came thanks to this compound. Stuff dried almost before a dust speck could land. This isn’t just about home DIY either. A lot of commercial paint brands depend on butyl acetate to meet expectations for fast turnaround.
Step into a nail salon and the scent lingers again. Nail polish formulas often include butyl acetate because it helps the color flow, dry fast, and last longer. It’s tough to imagine modern nail art without it. The mix also helps polish resist clumping and keeps the sparkle suspended. Nail professionals rely on these features a lot, especially during busy weekend appointments.
Major manufacturers count on butyl acetate not just for looks, but for real performance. Cars, furniture, and even electronics sport coatings made possible with help from this solvent. In large-scale manufacturing, having a solvent that leaves a smooth, sturdy finish is important. Most factory workers can confirm how quickly you can move a product down the line thanks to faster drying times. The less time waiting for layers to cure, the more units can head out the door.
Printing ink is another frequent use. Printers deal with deadlines and big runs. Butyl acetate helps ensure the ink dries before the next pages stack up. Newspapers and magazines stay smudge-free, and glossy labels look sharp. Lab tests often show butyl acetate boosting clarity and adhesion too.
Not everyone knows that butyl acetate also plays a part in food science. Flavor companies use it to add fruity notes to candies and snacks. That burst of apple or banana that comes through in some gum or hard candy? It often traces back to this compound, diluted and blended safely following regulations. Same story for perfumes and body sprays. A lot of scent developers appreciate how it helps fragrances mellow out without overpowering the other ingredients. Perfumers talk a lot about finding the right solvent to keep a blend consistent. Butyl acetate steps up where some others can’t.
With all these uses, problems can also creep in. Anyone who’s worked with strong-smelling solvents knows that fumes make for harsh air, especially in closed rooms. I remember long paint jobs in badly ventilated basements—headaches come quick. Frequent exposure can bother eyes, skin, and lungs, and there’s always debate around long-term safety. Workers in nail salons often ask for better protections, like stronger ventilation or safer alternatives, to cut down on daily exposure.
Regulation starts at industrial scale, with safety standards calling for proper exhaust systems and careful storage. Some startups chase water-based paints and polishes to steer clear of solvents altogether. Going forward, companies and regulators have a job to do—finding balances between reliable performance and fewer health risks. This is where investment in greener chemistry makes a lot of sense. Less harmful solvents, smarter packaging, and protective gear for workers can all help lighten the downsides that come with such a useful chemical.
Butyl acetate shows up in places most people never think about. Grab a can of nail polish remover or a glossy new paint, and odds are, you've met this chemical. It's used for that sharp, fruity smell in many manufactured products. Some people catch a whiff near certain cleaning supplies or even art studios filled with paint thinners. This isn’t a niche chemical—it's part of how modern goods get made and delivered.
The real trouble with butyl acetate starts with breathing it in or letting it touch your skin, especially at work or in tight rooms. Inhaling the vapors makes a lot of folks dizzy, gives them headaches, or messes with their noses and throats. You gulp enough of this stuff, your stomach can revolt—nausea, maybe even vomiting. Let it touch your skin and you might get a nasty rash or irritation. Some people see their symptoms get worse after repeated exposure, so the risks grow with frequent contact.
Walk into any woodworking shop using finishes, and people tend to shrug off the smell. The real risk comes from enclosed spaces, people pushing to finish the job, windows closed, maybe a fan or two running, but air never really clearing out the room. After a few hours, your brain gets foggy, eyes sting, and lungs protest. That’s not just discomfort—long-term exposure has potential to damage the nervous system, and nobody wants that trophy for putting in long hours on the job.
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists sets the recommended limit for butyl acetate exposure at around 150 parts per million over an 8-hour workday. Most homes or public spaces never reach these numbers. But a stubborn garage painter, churning through can after can with no respirator and poor ventilation, can get those levels in no time.
A friend of mine once worked in a nail salon just to cover college tuition. She remembers the constant, sweet, biting odor—the kind that sticks in your nose long after you leave. After a few months, she started noticing her hands were always dry and red, with a scratchy throat most mornings. Back then, nobody thought about fume hoods or proper gloves. Years later, she swears the memories alone trigger headaches.
People can make smarter choices to stay safe. Cracking a window isn’t enough if you use solvents for hours. Proper ventilation matters. Industrial shops use exhaust fans. Hobbyists, artists, and home renovators should look for masks rated for organic vapors and wear gloves when their hands touch the stuff. If possible, switch to water-based or less-toxic formulas—there are many available now, and they don’t bring the same risks to your home or workspace.
Read product labels, too. A little effort here stops headaches and health scares from stopping you later on. Keeping work surfaces clean and covered, cleaning skin quickly if you spill, and taking regular breaks outside gives your body a chance to recover. These are simple changes, not big expenses.
Employers and business owners bear responsibility as well. The cost of investing in protective gear or better ventilation pays off in less sick time and healthier workers. Training staff not just to use, but to respect the hazards in common chemicals, leads to fewer accidents. Big changes don’t always start from safety inspectors or government rulebooks. Sometimes, people just need to look at what’s happening around them and care enough to reduce the risks for everyone.
Walk into almost any auto body garage, and you catch a whiff of something sweet and fruity. That’s probably butyl acetate, a clear liquid that punches way above its weight in the world of solvents. Instead of blending in like other chemicals, butyl acetate makes itself known by quickly evaporating and leaving little behind but that distinct pear-drop aroma. For lots of folks working in manufacturing or art studios, this scent is practically tied to getting a job done.
Butyl acetate reminds me of summertime—light, volatile, always moving. With a boiling point just above 126°C, it heads for the air unless you put a tight lid on it. This makes cleanup fast but safety a bigger deal. On a cold morning, it turns sluggish, freezing up below -77°C. Pouring from the bottle, it spreads easily thanks to its low viscosity, although it doesn’t mix with water. Pour some in a cup of water, and it’ll float on top, refusing to dissolve—a handy trick if you need to separate it for recycling.
Pick up a bottle and shake it around. It won’t weigh you down—that’s because its density falls below that of water, right around 0.88 grams per cubic centimeter. This matters whether you’re measuring by weight behind a factory counter or timbering gallons for a big painting project. Precision gets tricky: even a little spillage can throw off recipes in the lab or in a nail salon mixing station. Relying on the senses works in a pinch, but getting reliable equipment is a smarter bet if you handle it every day.
Butyl acetate likes to play with other organic solvents. If you need a paint to dry smooth or an ink to glide across a page, manufacturers reach for it. The ester structure hiding in those sweet fumes (butanol linked to acetic acid) means it reacts under the right circumstances—just watch what you mix it with. Tossing it around with strong acids or bases can start an unwanted transformation. Add heat, and those vapors become highly flammable, posing real danger in close quarters. I learned early on: even that fresh, fruity smell should serve as a warning. Left unchecked, fumes can build up, causing headaches or worse, so cracking a window or wearing a mask isn’t just some regulation, it’s smart.
Most of us don’t see the “behind-the-scenes” role butyl acetate plays. It keeps paint smooth and dries print jobs fast. Businesses pick it for its just-right evaporation speed and its ability to make pigments and binders come together in a way that lasts. Regulations from groups like OSHA remind us this isn’t the kind of liquid to leave uncapped. Proper storage in cool, ventilated places prevents accidental fires and makes cleanup easier in case someone drops a bottle.
Every time I work near chemicals like this, I spot lessons for safer, smarter use. Swapping open containers for ones with sealing lids keeps fumes down and product fresher. Spills happen, but simple absorbent pads or a ready spill kit can stop a minor accident from spiraling. Training goes a long way. Anyone who works regularly with butyl acetate learns the signs of overexposure—dizziness, headaches, things you might brush off at first but shouldn’t. For small businesses, partnering with local safety pros or trade groups can mean the difference between a smooth operation and a costly mistake. In bigger plants, investment in air filtration isn’t overkill—it’s a basic way to protect workers and stay in business.
Butyl acetate shows up in everything from nail polish remover to industrial coatings. This chemical might seem harmless in small bottles on a beauty shelf, but in bulk, it takes real care to keep it safe, both for workers and for the environment. One spill, one careless move, and you’re staring at a room full of flammable vapors or a trip to the emergency room. After a few years in a warehouse and handling a whole lot of flammable liquids, I’ve seen what cutting corners can lead to. That experience always reminds me that butyl acetate isn’t just a line on a safety sheet; it’s a chemical that needs respect every single day.
Anyone opening a drum of butyl acetate catches that strong, fruity smell right away. It’s the first sign this stuff wants to escape into the air. Let it build up, and basic tasks suddenly seem a lot more dangerous. Back in the early days, a colleague forgot to switch on the ventilation. Within half an hour, we all felt dizzy and headaches crept up. That scare put proper airflow at the top of our safety list.
It’s tempting to store chemicals wherever there’s a bit of space, but this liquid demands a cool, dry area, away from sunlight and anything that can spark. Putting it next to heat sources, electrical boxes, or even direct sunlight is asking for an accident. It doesn’t take a degree in chemistry to see that a single mistake could mix butyl acetate fumes with electricity or flames. Most safety incidents come from simple oversights like that.
On the floor, we stick with metal containers that seal tight, not plastics that might soften or leak. I’ve learned that labeling every barrel clearly and keeping an updated inventory helps avoid dangerous mix-ups. You’d be surprised how common it is for workers to grab the wrong container during a busy shift. Shelving stays grounded, and we always space drum containers for easier access in emergencies. Locking up the storage area stops unauthorized folks from poking around where they have no business.
Routine checks play a major role. Every week, we make a point of looking for leaks, corrosion, or anything else out of place. If any drum seems compromised, it gets moved out and handled before a small problem turns into a big one. We don’t allow food, drink, or casual lounging nearby. No one wants to risk ingesting toxic vapor or contaminating a lunch break.
Gloves, goggles, and a sturdy apron protect from splashes—no exceptions. A well-fitting respirator makes the difference, especially in tight indoor spots. I keep spill kits within reach, stocked with absorbent pads, neutralizing agents, and disposal bags. We run spill drills every few months; practice makes real emergencies far less terrifying.
Transporting butyl acetate doesn’t get rushed. Lift carefully, use the right trolleys, and avoid dragging containers across rough floors. That way, minor drops don’t turn into gushing leaks. We use designated routes for chemical movement, keeping paths clear of clutter. One shortcut might save a minute, but the risks just aren’t worth it.
Most warehouse teams rely on clear guidelines, regular training, and honest, open communication. A noticeboard with up-to-date safety info, an open-door policy for raising concerns, and a system for reporting near-misses encourage everyone to stay alert. In high-stakes environments like this, one person’s carelessness can affect everyone. Relying on habits, rather than paper protocols alone, helps create a culture where chemical safety and respect for butyl acetate become second nature.
If you’ve ever cracked open a drum of butyl acetate, you know it smells like nail polish remover on steroids. You keep it sealed and out of the sun, thinking it'll last forever. It’s tempting to treat chemicals like rocks—solid, permanent, expiration date just a suggestion. The reality feels different the moment you find gunky bottles in the back of a workshop, labels curling, liquid cloudy.
Let’s talk numbers. Most manufacturers set the shelf life of butyl acetate around two to five years. That estimate isn’t just covering their backs. Butyl acetate starts to lose its punch as soon as it leaves that tightly-sealed factory container. If you break the seal and keep letting in oxygen or moisture, the clock ticks even faster. Temperature swings and leaky caps push that “best by” date even closer.
In my days working at a small paint shop, we watched old butyl acetate turn. You notice the smell changes, the clarity fades, filters start clogging. Most of us shrug it off—who’s checking expiry dates in the middle of a project? The problem sneaks up when batches don’t dry right, coatings get sticky, or colors warp. The cost isn’t just one shipment wasted; it’s time spent tracking weird failures and frustrated calls to suppliers.
Air and water do the job best. Butyl acetate likes dry, sealed, and cool places. Stash it near a window or under a vent, it absorbs moisture and degrades faster. Metal drums with rusty lids or plastic bottles set too close to the warehouse heater—those are the ones you open and grimace at the vinegary whiff. Even small leaks build up. Ever worked with off-smelling solvent? Projects turn into headaches and nobody trusts your results.
It always helps to take a look and a whiff. Is it cloudy? Any suspicious floaties? Smell sweeter than normal or a bit sour? Don’t ignore those hints. Some labs recommend running a quick purity check for big batches, but most smaller shops rely on experience—if it looks off, get rid of it.
You don’t need a high-end lab to keep your chemicals in shape. Just pick a spot that stays pretty steady in temperature, toss a note on every container with the date it was opened, and make sure lids are tight every time. If you finish a container, rinse and close its replacement right away. Rotation sounds fancy, but it’s as simple as using the oldest ones first, never letting the same can collect dust year after year.
Wasted butyl acetate isn’t just a hassle—it costs money. Making smaller, more frequent buys helps avoid stockpiles that quietly spoil. Work with suppliers willing to offer flexible delivery and clear labeling so you know exactly what’s fresh. Some companies even take back unopened, outdated drums. It’s easier than gambling on whether that five-year-old bottle will mess up the whole job.
A little attention pays dividends. Keep chemicals dry, cool, and sealed. Treat expired solvents with suspicion, not nostalgia. Five years is plenty—after that, you’re taking risks you just don’t need when quality’s on the line.
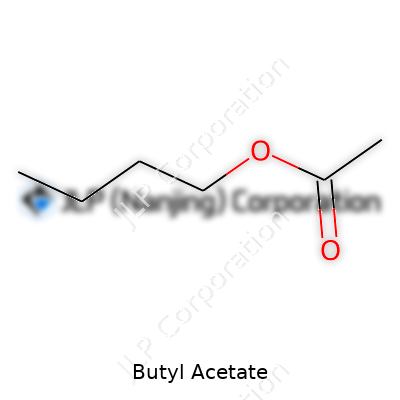
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | Butyl ethanoate |
| Other names |
Acetic acid butyl ester Butyl ethanoate n-Butyl acetate Butylester kyseliny octove BA |
| Pronunciation | /ˈbjuːtɪl əˈsiːteɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 123-86-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1901407 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:31328 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL14001 |
| ChemSpider | 6828 |
| DrugBank | DB02197 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03e349e3-3f49-4871-8725-6ceebb4219a2 |
| EC Number | 204-658-1 |
| Gmelin Reference | 803 |
| KEGG | C06355 |
| MeSH | D001972 |
| PubChem CID | 31272 |
| RTECS number | AF7350000 |
| UNII | 7HQO4QVR1U |
| UN number | 1123 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless transparent liquid |
| Odor | fruity odor |
| Density | 0.882 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | 0.68 g/100 mL (20 °C) |
| log P | 1.78 |
| Vapor pressure | 11.5 mmHg @ 20°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ 25 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 15.5 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -46.5e-6 cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.394 |
| Viscosity | 0.74 mPa·s (at 25°C) |
| Dipole moment | 1.84 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 229.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −486.6 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -2690 kJ·mol⁻¹ |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | D01AE19 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H319, H336 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P312, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | NFPA 704: 2-3-2 |
| Flash point | 27 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 421 °C |
| Explosive limits | 1.7–8.0% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral, rat: 10768 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): 10,760 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | XA9275000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 150 ppm |
| REL (Recommended) | 150 ppm |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 1700 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Acetic acid n-Butanol Isobutyl acetate Ethyl acetate Propyl acetate Methyl acetate |